3 分钟
Linux Shell 初始化文件 —— 环境变量写在哪里?
流程图
大差不差,请以自己机器为准
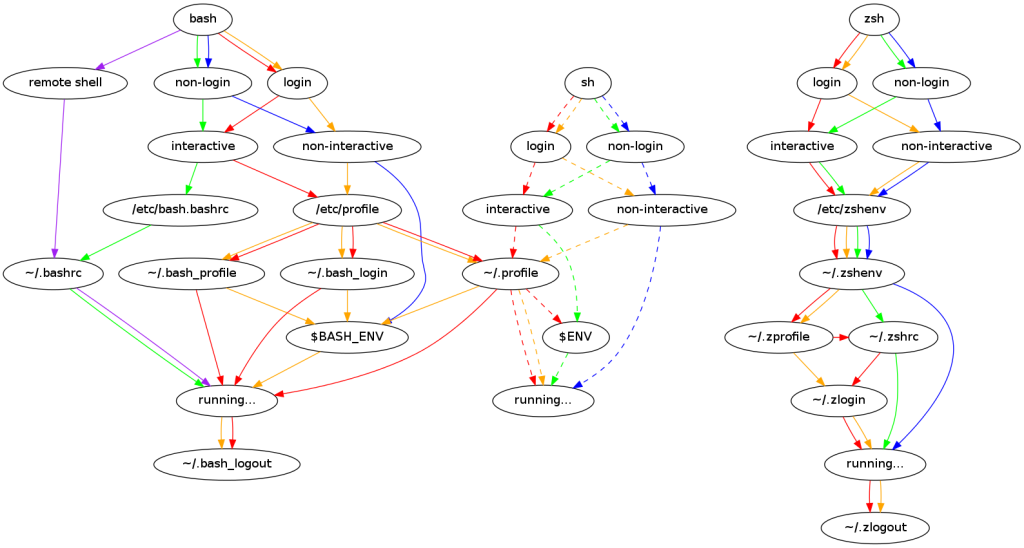
Shell 四种模式
不同的模式,执行的初始化脚本不同
- 登录交互式:登录系统得到的第一个终端(tty、本地、SSH 都是的)
- 非登录交互式:Linux GUI 打开的终端窗口;直接执行
bash进入的 shell。 - 非登录非交互:
.sh脚本执行所在的环境ssh user@remote script.sh
- 登录非交互:
- 在脚本中通过
#!/bin/bash --login头指定 ssh user@remote 非脚本的命令
- 在脚本中通过
判断一个 Shell 是否是登录式
- 方式 1:破坏性的,执行 logout 是否退出
- 方式 2:仅支持 Bash,
shopt login_shell - 方式 3:仅支持 Bash 和 ZSH
[[ -o login ]]
判断一个 Shell 是否是交互式
- 方式 1:通用,
$-环境变量是否包含i字符 - 方式 3:仅支持 Bash 和 ZSH,通过判断
$PS1是否存在判断(sh 不支持)
实验过程
实验环境
Debian 9
准备
在所有初始化文件头部添加 Log
add_str_to_file_head_if_not_exist(){
str=$1
f=$2
grep -F -q "$str" $f || printf '%s\n%s\n' "$str" "$(cat $f)" | sudo tee $f
}
# bash
add_str_to_file_head_if_not_exist 'echo "[source] /etc/profile"' /etc/profile
echo 'echo "[source] /etc/profile.d/*"' | sudo tee /etc/profile.d/bash_init_test.sh
add_str_to_file_head_if_not_exist 'echo "[source] /etc/bash.bashrc"' /etc/bash.bashrc
add_str_to_file_head_if_not_exist 'echo "[source] ~/.bashrc"' ~/.bashrc
touch ~/.bash_profile && add_str_to_file_head_if_not_exist 'echo "[source] ~/.bash_profile"' ~/.bash_profile
touch ~/.bash_logout && add_str_to_file_head_if_not_exist 'echo "[source] ~/.bash_logout"' ~/.bash_logout
# sh
add_str_to_file_head_if_not_exist 'echo "[source] ~/.profile"' ~/.profile
# zsh
add_str_to_file_head_if_not_exist 'echo "[source] /etc/zsh/zshenv"' /etc/zsh/zshenv
add_str_to_file_head_if_not_exist 'echo "[source] /etc/zsh/zlogin"' /etc/zsh/zlogin
add_str_to_file_head_if_not_exist 'echo "[source] /etc/zsh/zprofile"' /etc/zsh/zprofile
add_str_to_file_head_if_not_exist 'echo "[source] /etc/zsh/zlogout"' /etc/zsh/zlogout
add_str_to_file_head_if_not_exist 'echo "[source] /etc/zsh/zshrc"' /etc/zsh/zshrc
add_str_to_file_head_if_not_exist 'echo "[source] ~/.zshrc"' ~/.zshrc
touch ~/.zshenv && add_str_to_file_head_if_not_exist 'echo "[source] ~/.zshenv"' ~/.zshenv
touch ~/.zprofile && add_str_to_file_head_if_not_exist 'echo "[source] ~/.zprofile"' ~/.zprofile
touch ~/.zlogin && add_str_to_file_head_if_not_exist 'echo "[source] ~/.zlogin"' ~/.zlogin
touch ~/.zlogout && add_str_to_file_head_if_not_exist 'echo "[source] ~/.zlogout"' ~/.zlogout测试 zsh
准备
sudo usermod -s /bin/zsh $(whoami)登录交互式
ssh $(whoami)@localhost
# 输出如下
# [source] /etc/zsh/zshenv
# [source] ~/.zshenv
# [source] /etc/zsh/zprofile
# [source] ~/.zprofile
# [source] /etc/zsh/zshrc
# [source] ~/.zshrc
# [source] /etc/zsh/zshenv
# [source] /etc/zsh/zlogin
# [source] ~/.zlogin非登录交互式
zsh
# 输出如下
# [source] /etc/zsh/zshenv
# [source] ~/.zshenv
# [source] /etc/zsh/zshrc
# [source] ~/.zshrc非登录非交互式
zsh -c ""
# 输出如下
# [source] /etc/zsh/zshenv
# [source] ~/.zshenv登录非交互
zsh -c --login ""
# 输出如下
# [source] /etc/zsh/zshenv
# [source] ~/.zshenv
# [source] /etc/zsh/zprofile
# [source] ~/.zprofile
# [source] /etc/zsh/zlogin
# [source] ~/.zlogin测试 bash
准备
sudo usermod -s /bin/bash $(whoami)登录交互式
ssh $(whoami)@localhost
# 输出如下
# [source] /etc/profile
# [source] /etc/bash.bashrc
# [source] /etc/profile.d/*
# [source] ~/.bash_profile非登录交互式
bash
# 输出如下
# [source] /etc/bash.bashrc
# [source] ~/.bashrc非登录非交互式
bash -c ""
# 没有输出,会执行 $BASH_ENV登录非交互
bash -c --login ""
# 输出如下
# [source] /etc/profile
# [source] /etc/profile.d/*
# [source] ~/.bash_profile测试 sh
略
常见问题和建议
SSH直接执行脚本环境变量的问题
参考:问答
- 将本地文件在远端执行:非交互登录模式
ssh remote < 本地文件.sh
- 直接执行远端文件:非交互非登录模式(可能存在环境变量问题)
ssh remote '远端文件.sh'
- 直接执行远端文件:非交互登录模式
ssh remote 'bash --login 远端文件.sh'
- 伪终端模式:
ssh -t remote
报告 Command not found,但是登录
原因在于 Shell 的四种模式执行的初始化文件不同,解决方案参见
不要使用 /bin/sh
/bin/sh 能力较弱不要使用
如果导出自己的环境变量
考虑兼容 zsh 和 bash 的四种模式,防止因为模式不同导致的
- 在家目录添加自己的环境变量脚本 比如
~/.my_env - 在
~/.bashrc、~/.zshenv、~/.profile中添加source ~/.my_env - 如果存在
~/.bash_profile,请检查~/.bash_profile中是否包含source ~/.bashrc若没有,需要加上
另外,不要使用 非登录非交互式 的 顶级 shell 执行命令(顶级 shell 指其祖宗进程都是非登录非交互式的,无法继承环境变量)
交互式 Shell 环境
推荐使用 zsh,原因在于体验好
自动化脚本 Shell 环境
推荐使用 bash,原因在于兼容性好且能力够用