23 分钟
scala读书笔记(二)
代码优于描述
七、集合概况
1、集合分类
(1)scala集合按照是否可变分为可变Mutable和不可变Immutable
(2)scala集合按类型分为
- 序列
- set
- map
(3)序列
通用集合
| Immutable不可变 | Mutable可变 | |
|---|---|---|
| Indexed索引 | Vector | ArrayBuffer |
| 链表 | List | ListBuffer |
主要不可变集合scala.collection.immutable
| 索引序列 | 链表序列 | 描述 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| List | ✓ | 单链表 | |
| Queue | ✓ | 队列 | |
| Range | ✓ | 整数值范围 | |
| Stack | ✓ | 栈 | |
| Stream | ✓ | 类似于链表,lazy特性 | |
| String | ✓ | java String | |
| Vector | ✓ | 可索引序列 |
主要可变集合scala.collection.mutable
| 索引序列 | 链表序列 | 描述 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Array | ✓ | 依赖java数组实现,元素可变,大小不可变 | |
| ArrayBuffer | ✓ | 数组实现 | |
| ArrayStack | ✓ | 数组实现栈 | |
| DoubleLinkedList | ✓ | 双向链表 | |
| LinkedList | ✓ | 可变单链表 | |
| ListBuffer | ✓ | ||
| MutableList | ✓ | ||
| Queue | ✓ | 队列 | |
| Stack | ✓ | ||
| StringBuilder | ✓ | java里StringBuilder |
(4)Map
| 不可变 | 可变 | 描述 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HashMap | ✓ | ✓ | |
| LinkedHashMap | ✓ | ||
| ListMap | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Map | ✓ | ✓ | |
| SortedMap | ✓ | ||
| TreeMap | ✓ | 红黑树实现 | |
| WeakHashMap | ✓ | java.util.WeakHashMap的封装 |
(5)set
| 不可变 | 可变 | 描述 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BitSet | ✓ | ✓ | |
| HashSet | ✓ | ✓ | |
| LinkedHashSet | ✓ | ||
| ListSet | ✓ | ||
| TreeSet | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Set | ✓ | ✓ | |
| SortedSet | ✓ | ✓ | 略 |
(6)其他
| 描述 | |
|---|---|
| Enumeration | 一个包含常数值的有限集合 |
| Iterator | 迭代器 |
| Option | 包含一个或零个元素的集合 |
| Tuple | 元组,支持异构元素的集合,最多支持22个元素 |
2、集合方法
(1)集合方法分类
- 过滤方法
- collect, diff, distinct, drop, dropWhile, filter, filterNot, find, foldLeft, foldRight, head, headOption, init, intersect, last, lastOption, reduceLeft, reduceRight, remove, slice, tail, take, takeWhile, and union.
- 转换方法
- +, ++, −, −−, diff, distinct, collect, flatMap, map, reverse, sortWith, takeWhile, zip, and zipWithIndex.
- 分组方法
- groupBy, partition, sliding, span, splitAt, and unzip
- 信息和数学方法
- canEqual, contains, containsSlice, count, endsWith, exists, find, forAll, hasDefiniteSize, indexOf, indexOfSlice, indexWhere, isDefinedAt, isEmpty, lastIndexOf, lastIndexOfSlice, lastIndexWhere, max, min, nonEmpty, product, segmentLength, size, startsWith, sum.
- 其他
- par, view, flatten, foreach, mkString.
以下列表说明
- c 代表集合
- f 代表函数
- p 代表谓词(返回Boolean的函数)
- n 代表数字
- op代表简单操作(通常是一个简单函数)
(2)遍历集合常用方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| c collect f | 集合c中每一个元素通过偏函数f返回值构成一个新集合 |
| c count p | 对满足谓词条件的元素计数 |
| c1 diff c2 | 返回c1中c2中没有的元素 |
| c drop n | 返回集合去掉前n个元素的集合 |
| c dropWhile p | 返回移除满足谓词p最长前缀的集合,去掉返回第一个false之前的元素 |
| c exists p | 如果元素每个元素都满足p,则返回true,否则false |
| c filter p | 返回p为true的所有元素 |
| c filterNot p | 返回p为false的所有元素 |
| c find p | 返回第一个满足p的元素的Option否则返回None |
| c flatten | 将两层list展开一层 |
| c flatMap | 对每一个元素做map,然后执行flatten |
| c foldLeft(z)(op) | 将操作应用于上一次执行的结果和当前元素,z和第一个元素操作,从左到右返回类型和z相同 |
| c foldRight(z)(op) | 类似上,从右到左 |
| c forAll p | 如果所有元素都满足p则返回true,否则返回false |
| c foreach f | foreach |
| c groupBy f | 把集合归类成Map,根据f返回值作为key,同一个key的元素的集合作为value |
| c hasDefiniteSize | 测试元素是否有限 |
| c head | 返回集合第一个元素,如果集合为空抛出 NoSuchElementException |
| c headOption | 返回Option |
| c init | 返回出去最后一个元素的集合,集合为空抛出UnsupportedOperationException |
| c1 intersect c2 | 返回连个集合的交集 |
| c isEmpty | 是否为空 |
| c last | 返回最后一个元素,如果集合为空抛出 NoSuchElementException |
| c lastOption | 返回最后一个元素的Option |
| c map f | 函数f应用于每一个元素返回值的集合 |
| c max | 返回最大 |
| c min | 返回最小 |
| c nonEmpty | 非空返回true |
| c par | 返回集合的并行实现,创建在新的线程中?? |
| c partition p | 根据谓词返回两个集合的元组 |
| c product | 返回所有元素的乘积 |
| c reduceLeft op | 类似于foldLeft,从第一个元素开始 |
| c reduceRight op | 类似于foldRight,从最后一个元素开始 |
| c reverse | 集合倒序 |
| c size | 集合的大小 |
| c slice(from, to) | 返回from到to的间隔,区间为[from,to) |
| c sortWith f | 返回按照函数f的排序 |
| c span p | 返回 c.takeWhile(p) 和 c.dropWhile(p)的并集 |
| c splitAt | 在n位置拆分一个集合,返回一个由两个集合组成的元组 |
| c sum | 返回集合所有元素的和 |
| c tail | 返回除第一个元素外的其他元素组成的集合 |
| c take n | 返回前n个元素的结合 |
| c takeWhile p | 返回为true时的集合元素,false时停止 |
| c1 union c2 | 返回两个集合的并集 |
| c unzip | ?? |
| c view | 返回集合的一个非严格lazy视图 |
| c1 zip c2 | 按对匹配, 返回(c1(0),c2(0)),(c1(1),c2(1))… |
| c zipWithIndex | 按照下标遍历集合,返回一个元组集合 |
(3)可变集合中常用操作符
| 操作符 (方法) | 描述 |
|---|---|
| c += x | 把元素x添加到元素c |
| c += (x,y,z) | 把x,y,z添加到元素c |
| c1 ++= c2 | 把c2元素添加到c1中 |
| c −= x | 从集合c中删除元素x |
| c −= (x,y,z) | 从集合c中删除x,y,z |
| c1 −−= c2 | 从c1中删除c2中的所有元素 |
| c(n) = x | 将值x赋给c(n) |
| c clear | 清空所有元素 |
| c remove n | 删除位置为n的元素 |
| c.remove(n, len) | 从n位置删除len长度的元素 |
(4)不可变集合中常用操作符
| 操作符 (方法) | 描述 |
|---|---|
| c1 ++ c2 | c2附加到c1中创造新的集合 |
| c :+ e | 把e附加到c中,并创建新元素 |
| e +: c | 将元素e插到c的首部返回一个新集合 |
| e :: list | 同上,在List有用 |
| c drop n | |
| c dropWhile p | |
| c filter p | |
| c filterNot p | |
| c head | |
| c tail | |
| c take n | |
| c takeWhile p | 见上 |
(5)map方法
不可变map方法
| 操作符 (方法) | 描述 |
|---|---|
| m - k | 删除key后map |
| m - (k1, k2, k3) | 返回删除k1,k2,k3的map |
| m – c | 删除序列内的key |
可变map方法
| 操作符 (方法) | 描述 |
|---|---|
| mm += (k -> v) | 把k->v添加到map中 |
| mm += (k1 -> v1, k2 -> v2) | |
| mm ++= c | 将集合c中的pair添加到map中 |
| mm ++= List(3 -> “c”) | |
| mm -= k | 将map中k对应的k->v删除 |
| mm -= (k1, k2, k3) | |
| mm –= c | 将集合c中的key从map中删除 |
map不可变和可变共有方法
| 操作符 (方法) | 描述 |
|---|---|
| m(k) | 根据k访问v |
| m contains k | 返回是否包含k |
| m filter p | 返回满足p条件的键值 |
| m filterKeys p | 返回包含匹配谓词p条件的key的map |
| m get k | 返回Option |
| m getOrElse(k, d) | 如果存在k返回v,否则返回默认值d |
| m isDefinedAt k | 包含k返回true |
| m keys | 把keys作为Iterator返回 |
| m keyIterator | 把keys作为Iterator返回指向non-empty iterator |
| m keySet | 将key作为set返回 |
| m mapValues f | f函数应用map中每一个value,返回一个新map |
| m values | 把keys作为Iterator返回 |
| m valuesIterator | 把keys作为Iterator返回指向non-empty iterator |
3、集合的性能
前置说明
|Key |描述 | | – | ———————————— | |C |常数级| |eC |需要假设的常数时间| |aC |平均常数级| |Log |log复杂度| |L |常数级复杂度| |- |不支持此操作|
性能特点
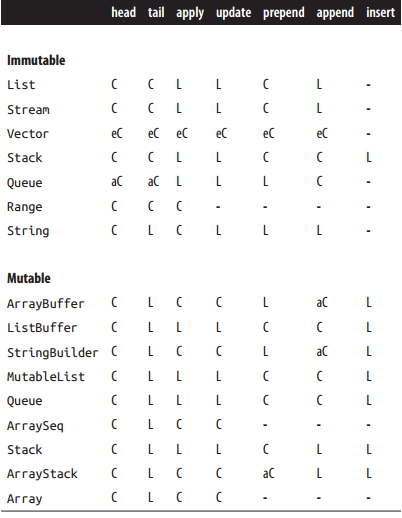
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| head | 返回第一个元素 |
| tail | 返回除第一个元素的集合 |
| apply | 索引 |
| update | 对于不可变序列的函数式更新,对可变序列的副作用更新 |
| prepend | 把元素添加到序列前面 |
| append | 把元素添加到序列尾部 |
| insert | 在序列中任意位置插入一个元素,只能在可变中使用 |
set/map性能特点
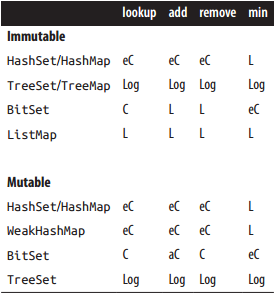
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| lookup | 看某个元素是否在set/map中 |
| add | 将新元素添加到set/map中 |
| remove | 删除一个元素 |
| min | 返回最小元素 |
4、创建序列
(1)创建集合声明类型(类似泛型)
val x = List[Number](1, 2.0, 33D, 400L)(2)不可变序列最佳选择
val v = Vector("a", "b", "c") //> v : scala.collection.immutable.Vector[String] = Vector(a, b, c)
//IndexedSeq的默认实现
val x = IndexedSeq(1,2,3) //> x : IndexedSeq[Int] = Vector(1, 2, 3)(3)可变序列的最佳选择
import scala.collection.mutable.ArrayBuffer
var nums = ArrayBuffer(1, 2, 3) //> nums : scala.collection.mutable.ArrayBuffer[Int] = ArrayBuffer(1, 2, 3)5、遍历集合
(1)使用foreach遍历集合
val x = Vector(1, 2, 3) //> x : scala.collection.immutable.Vector[Int] = Vector(1, 2, 3)
x.foreach((i: Int) => println(i)) //> 1
//| 2
//| 3(2)for遍历
val fruits = Traversable("apple", "banana", "orange")
//> fruits : Traversable[String] = List(apple, banana, orange)
for (f <- fruits) println(f) //> apple
//| banana
//| orange
//使用循环计数器
val fruits = Vector("apple", "banana", "orange") //> fruits : scala.collection.immutable.Vector[String] = Vector(apple, banana, o
//| range)
for (i <- 0 until fruits.size) println(s"element $i is ${fruits(i)}")
//> element 0 is apple
//| element 1 is banana
//| element 2 is orange(3)使用zipWithIndex或则zip创建循环计数器
zipWithIndex
val fruits = Vector("apple", "banana", "orange") //> fruits : scala.collection.immutable.Vector[String] = Vector(apple, banana, o
//| range)
fruits.zipWithIndex.foreach{case(e,i)=>println(s"index id $i, ele is $e")}
//> index id 0, ele is apple
//| index id 1, ele is banana
//| index id 2, ele is orangezip,指定计数器起始值
val fruits = Vector("apple", "banana", "orange") //> fruits : scala.collection.immutable.Vector[String] = Vector(apple, banana, o
//| range)
for ((elem, count) <- fruits.zip(Stream from 1)) {
println(s"element $count is $elem") //> element 1 is apple
//| element 2 is banana
//| element 3 is orange
}(4)迭代器遍历
//类java6、集合变换
(1)使用for/yield
val a = Array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5) //> a : Array[Int] = Array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
for (e <- a) yield e * 2 //> res0: Array[Int] = Array(2, 4, 6, 8, 10)(2)使用map方法实现集合变换
val helpers = Vector("adam", "kim", "melissa") //> helpers : scala.collection.immutable.Vector[String] = Vector(adam, kim, meli
//| ssa)
val caps = helpers.map(e => e.capitalize) //> caps : scala.collection.immutable.Vector[String] = Vector(Adam, Kim, Meliss
//| a)(3)列表扁平化
val lol = List(List(1,2), List(3,4)) //> lol : List[List[Int]] = List(List(1, 2), List(3, 4))
val result = lol.flatten //> result : List[Int] = List(1, 2, 3, 4)(4)flatMap(f) === map(f).flatten
val bag = List("1", "2", "three", "4", "one hundred seventy five")
//> bag : List[String] = List(1, 2, three, 4, one hundred seventy five)
def toInt(in: String): Option[Int] = {
try {
Some(Integer.parseInt(in.trim))
} catch {
case e: Exception => None
}
} //> toInt: (in: String)Option[Int]
bag.flatMap(toInt).sum //> res0: Int = 7
bag.map(toInt).flatten.sum //> res1: Int = 7(5)过滤、提取集合
collect, diff, distinct,
drop, dropWhile, filter, filterNot, find, foldLeft, foldRight, head,
headOption, init, intersect, last, lastOption, reduceLeft, reduceRight,
remove, slice, tail, take, takeWhile, union(6)集合分割(groupBy,parttition)
groupBy返回map
val x = List(15, 10, 5, 8, 20, 12) //> x : List[Int] = List(15, 10, 5, 8, 20, 12)
val y = x.groupBy(_ > 10) //> y : scala.collection.immutable.Map[Boolean,List[Int]] = Map(false -> List(10
//| , 5, 8), true -> List(15, 20, 12))partition返回元组,按照true,false分组
val x = List(15, 10, 5, 8, 20, 12) //> x : List[Int] = List(15, 10, 5, 8, 20, 12)
val y = x.partition(_ > 10) //> y : (List[Int], List[Int]) = (List(15, 20, 12),List(10, 5, 8))span返回元组,分为满足谓词的最长前缀和剩下元素两组
val x = List(15, 10, 5, 8, 20, 12) //> x : List[Int] = List(15, 10, 5, 8, 20, 12)
val y = x.span(_ < 20) //> y : (List[Int], List[Int]) = (List(15, 10, 5, 8),List(20, 12))x.splitAt(2)返回元组,按照位置
val x = List(15, 10, 5, 8, 20, 12) //> x : List[Int] = List(15, 10, 5, 8, 20, 12)
val y = x.splitAt(2) //> y : (List[Int], List[Int]) = (List(15, 10),List(5, 8, 20, 12))sliding(size, step) | sliding(size)
val nums = (1 to 5).toArray //> nums : Array[Int] = Array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
nums.sliding(2).toList //> res0: List[Array[Int]] = List(Array(1, 2), Array(2, 3), Array(3, 4), Array(4,
//| 5))
nums.sliding(2, 2).toList //> res1: List[Array[Int]] = List(Array(1, 2), Array(3, 4), Array(5))
nums.sliding(2, 3).toList //> res2: List[Array[Int]] = List(Array(1, 2), Array(4, 5))zip两个列表按照idx配对组成新的列表,unzip反之
val women = List("Kim", "Julia") //> women : List[String] = List(Kim, Julia)
val men = List("Al", "Terry") //> men : List[String] = List(Al, Terry)
val couples = women zip men //> couples : List[(String, String)] = List((Kim,Al), (Julia,Terry))
couples.unzip //> res0: (List[String], List[String]) = (List(Kim, Julia),List(Al, Terry))(7)reduce和fold方法
略
(8)提取不重复元素
val x = Vector(1, 1, 2, 3, 3, 4) //> x : scala.collection.immutable.Vector[Int] = Vector(1, 1, 2, 3, 3, 4)
val y = x.distinct //> y : scala.collection.immutable.Vector[Int] = Vector(1, 2, 3, 4)(9)序列合并
- ++=合并为可变集合
- ++ 合并集合
- union并集,diff相对补集,intersect交集
- a ::: b 合并
(10)创建惰性视图view方法
(1 to 100).view //> res0: scala.collection.SeqView[Int,scala.collection.immutable.IndexedSeq[Int]
//| ] = SeqView(...)7、创建集合
(1)利用Range创建集合
Array.range(1, 5) //> res0: Array[Int] = Array(1, 2, 3, 4)
List.range(0, 10) //> res1: List[Int] = List(0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9)
Vector.range(0, 10, 2) //> res2: scala.collection.immutable.Vector[Int] = Vector(0, 2, 4, 6, 8)(2)枚举
object Margin extends Enumeration {
type Margin = Value
val TOP, BOTTOM, LEFT, RIGHT = Value
}
Margin.TOP //> res0: worksheet.Margin.Value = TOP(3)元组
val d = ("Debi", 95) //> d : (String, Int) = (Debi,95)
case class Person(name: String)
val t = (3, "Three", new Person("Al")) //> t : (Int, String, worksheet.Person) = (3,Three,Person(Al))
t._1 //> res0: Int = 3
t._3 //> res1: worksheet.Person = Person(Al)
val (x, y, z) = (3, "Three", new Person("Al"))
//> x : Int = 3
//| y : String = Three
//| z : worksheet.Person = Person(Al)
val (x1, _, _) = t //> x1 : Int = 3
val b = "AL" -> "Alabama" //> b : (String, String) = (AL,Alabama)8、集合排序
val a = List(10, 5, 8, 1, 7).sorted //> a : List[Int] = List(1, 5, 7, 8, 10)
val b = List("banana", "pear", "apple", "orange").sorted
//> b : List[String] = List(apple, banana, orange, pear)
List(10, 5, 8, 1, 7).sortWith(_ < _) //> res0: List[Int] = List(1, 5, 7, 8, 10)
class Person(var name: String) extends Ordered[Person] {
override def toString = name
def compare(that: Person) = {
if (this.name == that.name)
0
else if (this.name > that.name)
1
else
-1
}
}
val ty = new Person("Tyler") //> ty : worksheet.Person = Tyler
val al = new Person("Al") //> al : worksheet.Person = Al
val paul = new Person("Paul") //> paul : worksheet.Person = Paul
val dudes = List(ty, al, paul) //> dudes : List[worksheet.Person] = List(Tyler, Al, Paul)
dudes.sorted //> res1: List[worksheet.Person] = List(Al, Paul, Tyler)9、将集合转换为字符串,mkString
val a = Array("apple", "banana", "cherry")//> a : Array[String] = Array(apple, banana, cherry)
a.mkString //> res0: String = applebananacherry
a.mkString(" ") //> res1: String = apple banana cherry
a.mkString(", ") //> res2: String = apple, banana, cherry
a.mkString("[", ", ", "]") //> res3: String = [apple, banana, cherry]八、列表、数组、映射、集及其他
1、列表(List、ListBuffer、Stream)
链表实现,头插尾插O(1) 适合递归
(1)创建与填充列表
创建不可变列表List
// 1
scala> val list = 1 :: 2 :: 3 :: Nil
list: List[Int] = List(1, 2, 3)
// 2
scala> val list = List(1, 2, 3)
x: List[Int] = List(1, 2, 3)
// 3a
scala> val x = List(1, 2.0, 33D, 4000L)
x: List[Double] = List(1.0, 2.0, 33.0, 4000.0)
322 | Chapter 11: List, Array, Map, Set (and More)
www.it-ebooks.info
// 3b
scala> val x = List[Number](1, 2.0, 33D, 4000L)
x: List[java.lang.Number] = List(1, 2.0, 33.0, 4000)
// 4
scala> val x = List.range(1, 10)
x: List[Int] = List(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9)
scala> val x = List.range(0, 10, 2)
x: List[Int] = List(0, 2, 4, 6, 8)
// 5
scala> val x = List.fill(3)("foo")
x: List[String] = List(foo, foo, foo)
// 6
scala> val x = List.tabulate(5)(n => n * n)
x: List[Int] = List(0, 1, 4, 9, 16)
// 7
scala> val x = collection.mutable.ListBuffer(1, 2, 3).toList
x: List[Int] = List(1, 2, 3)
// 8
scala> "foo".toList
res0: List[Char] = List(f, o, o)创建可变列表ListBuffer
import scala.collection.mutable.ListBuffer
var fruits = new ListBuffer[String]()
// add one element at a time to the ListBuffer
fruits += "Apple"
fruits += "Banana"
fruits += "Orange"(2)添加元素
val x = List(2) //> x : List[Int] = List(2)
val y = 1 +: x //> y : List[Int] = List(1, 2)
val z = 0 :: y //> z : List[Int] = List(0, 1, 2)(3)从List或ListBuffer删除元素
List
val originalList = List(5, 1, 4, 3, 2) //> originalList : List[Int] = List(5, 1, 4, 3, 2)
//通过filter删除
val newList = originalList.filter(_ > 2) //> newList : List[Int] = List(5, 4, 3)ListBuffer
import scala.collection.mutable.ListBuffer
val x = ListBuffer(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9)
//> x : scala.collection.mutable.ListBuffer[Int] = ListBuffer(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6,
//| 7, 8, 9)
//通过值删除
x -= 5 //> res0: worksheet.x.type = ListBuffer(1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9)
x -= (2, 3) //> res1: worksheet.x.type = ListBuffer(1, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9)
x --= Seq(1, 2, 3) //> res2: worksheet.x.type = ListBuffer(4, 6, 7, 8, 9)
//通过索引删除
x.remove(0) //> res3: Int = 4
x.remove(1, 3)(4)合并或连接列表
使用 ++,concat,:::方法
(5)使用List的lazy版本Stream
构造Stream
val s = 1#::2#::3#::Stream.empty
val s1 = (1 to 1000000000).toStream //不会爆内存2、数组(Array、ArrayBuffer)
编译成java的数组
(1)创建和更新
创建普通数组
val a = Array(1,2,3) //> a : Array[Int] = Array(1, 2, 3)
var a1:Array[String]=_
a1 = Array("apple","banana")
val a2 = Array.range(1,10) //> a2 : Array[Int] = Array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9)
val a3 = Array.range(0,10,2) //> a3 : Array[Int] = Array(0, 2, 4, 6, 8)
val a4 = Array.fill(3)("foo"); //> a4 : Array[String] = Array(foo, foo, foo)
val a5 = Array.tabulate(5)(n=>n*n) //> a5 : Array[Int] = Array(0, 1, 4, 9, 16)
val a6 = List(1,2,3).toArray //> a6 : Array[Int] = Array(1, 2, 3)
val a7 = "Hello".toArray //> a7 : Array[Char] = Array(H, e, l, l, o)创建可变数组ArrayBuffer
import scala.collection.mutable.ArrayBuffer
var c = ArrayBuffer[String]() //> c : scala.collection.mutable.ArrayBuffer[String] = ArrayBuffer()
c += "aa" //> res0: scala.collection.mutable.ArrayBuffer[String] = ArrayBuffer(aa)
c += "bb" //> res1: scala.collection.mutable.ArrayBuffer[String] = ArrayBuffer(aa, bb)
c ++=Seq("cc","dd") //> res2: scala.collection.mutable.ArrayBuffer[String] = ArrayBuffer(aa, bb, cc,
//| dd)
c.append("ee","ff")(2)删除元素
- ArrayBuffer使用
-=--=remove及clear - Array使用过滤方法和重新赋值方法
(3)排序
- 使用
scala.util.Sorting.quickSort(fruits); 使用
sorted、sortBy、sortWithval fruits = Array("cherry", "apple", "banana") //> fruits : Array[String] = Array(cherry, apple, banana) scala.util.Sorting.quickSort(fruits) println(fruits.toList); //> List(apple, banana, cherry) fruits.sorted //> res0: Array[String] = Array(apple, banana, cherry)
(4)创建多维数组
使用Array.ofDim()//非Array独有,最多允许5维
val rows = 2 //> rows : Int = 2
val cols = 3 //> cols : Int = 3
val a = Array.ofDim[String](rows, cols) //> a : Array[Array[String]] = Array(Array(null, null, null), Array(null, null,
//| null))
a(0)(0) = "a"
a(0)(1) = "b"
a(0)(2) = "c"
a(1)(0) = "d"
a(1)(1) = "e"
a(1)(2) = "f"
a //> res0: Array[Array[String]] = Array(Array(a, b, c), Array(d, e, f))使用数组的数组
val a = Array(Array("a", "b", "c"), Array("d", "e"))
//> a : Array[Array[String]] = Array(Array(a, b, c), Array(d, e))3、映射(Map)
(1)创建
创建不可变Map和可变映射区别在于导入包不同
val states = Map("AL" -> "Alabama", "AK" -> "Alaska")
//> states : scala.collection.immutable.Map[String,String] = Map(AL -> Alabama,
//| AK -> Alaska)
var states = collection.mutable.Map[String, String]()
//> states : scala.collection.mutable.Map[String,String] = Map()(2)选择Map实现
| 类或特质 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| collection.immutable.Map | 默认不可变映射 |
| collection.mutable.Map | 基本映射可变版本 |
| collection.mutable.LinkedHashMap | 遍历元素顺序为插入顺序 |
| collection.[mutable或immutable].ListMap | 基于List实现,元素插入到头部 |
| collection.SortedMap | 按Key排序 |
| collection.immutable.HashMap | 给予Hash查找树 |
| 查看doc文档 | ….. |
(3)添加、更新或删除元素
可变
var states = collection.mutable.Map[String, String]()
//> states : scala.collection.mutable.Map[String,String] = Map()
//添加或修改
states("AK") = "Alaska"
states += ("AL" -> "Alabama") //> res0: scala.collection.mutable.Map[String,String] = Map(AL -> Alabama, AK ->
//| Alaska)
states += ("AR" -> "Arkansas", "AZ" -> "Arizona")
//> res1: scala.collection.mutable.Map[String,String] = Map(AZ -> Arizona, AL ->
//| Alabama, AR -> Arkansas, AK -> Alaska)
states ++= List("CA" -> "California", "CO" -> "Colorado")
//> res2: scala.collection.mutable.Map[String,String] = Map(CO -> Colorado, AZ -
//| > Arizona, AL -> Alabama, CA -> California, AR -> Arkansas, AK -> Alaska)
//删除
states -= "AR" //> res3: scala.collection.mutable.Map[String,String] = Map(CO -> Colorado, AZ -
//| > Arizona, AL -> Alabama, CA -> California, AK -> Alaska)
states -= ("AL", "AZ") //> res4: scala.collection.mutable.Map[String,String] = Map(CO -> Colorado, CA -
//| > California, AK -> Alaska)
states --= List("AL", "AZ") //> res5: scala.collection.mutable.Map[String,String] = Map(CO -> Colorado, CA -
//| > California, AK -> Alaska)
//
states("AK") = "Alaska, A Really Big State"
states.put("CO", "Colorado") //> res6: Option[String] = Some(Colorado)
states.retain((k,v) => k == "AK") //> res7: scala.collection.mutable.Map[String,String] = Map(AK -> Alaska, A Real
//| ly Big State)
states.remove("AK") //> res8: Option[String] = Some(Alaska, A Really Big State)
states.clear不可变:使用var同样可以使用+= -=
val a = Map("AL" -> "Alabama") //> a : scala.collection.immutable.Map[String,String] = Map(AL -> Alabama)
//添加或更新
val b = a + ("AK" -> "Alaska") //> b : scala.collection.immutable.Map[String,String] = Map(AL -> Alabama, AK ->
//| Alaska)
val c = b + ("AR" -> "Arkansas", "AZ" -> "Arizona")
//> c : scala.collection.immutable.Map[String,String] = Map(AL -> Alabama, AK -
//| > Alaska, AR -> Arkansas, AZ -> Arizona)
val e = c - "AR" //> e : scala.collection.immutable.Map[String,String] = Map(AL -> Alabama, AK -
//| > Alaska, AZ -> Arizona)
val f = e - "AZ" - "AL" //> f : scala.collection.immutable.Map[String,String] = Map(AK -> Alaska)
var x = f; //> x : scala.collection.immutable.Map[String,String] = Map(AK -> Alaska)
x += ("AC" -> "AC");
println(x) //> Map(AK -> Alaska, AC -> AC)(4)访问映射的值
val states = Map("AL" -> "Alabama", "AK" -> "Alaska", "AZ" -> "Arizona")
//> states : scala.collection.immutable.Map[String,String] = Map(AL -> Alabama,
//| AK -> Alaska, AZ -> Arizona)
val s = states.getOrElse("FOO", "No such state")
//> s : String = No such state
val az1 = states.get("AZ") //> az1 : Option[String] = Some(Arizona)
val az2 = states.get("FOO") //> az2 : Option[String] = None
val az = states("AZ") //> az : String = Arizona
//不存在会抛异常
val ac = states("AC") //> java.util.NoSuchElementException: key not found: AC(5)遍历映射
val ratings = Map("Lady in the Water"-> 3.0,
"Snakes on a Plane"-> 4.0,
"You, Me and Dupree"-> 3.5) //> ratings : scala.collection.immutable.Map[String,Double] = Map(Lady in the W
//| ater -> 3.0, Snakes on a Plane -> 4.0, You, Me and Dupree -> 3.5)
for ((k,v) <- ratings) println(s"key: $k, value: $v")
//> key: Lady in the Water, value: 3.0
//| key: Snakes on a Plane, value: 4.0
//| key: You, Me and Dupree, value: 3.5
ratings.foreach {
case(movie, rating) => println(s"key: $movie, value: $rating")
} //> key: Lady in the Water, value: 3.0
//| key: Snakes on a Plane, value: 4.0
//| key: You, Me and Dupree, value: 3.5
ratings.foreach(x => println(s"key: ${x._1}, value: ${x._2}"))
//> key: Lady in the Water, value: 3.0
//| key: Snakes on a Plane, value: 4.0
//| key: You, Me and Dupree, value: 3.5
ratings.keys.foreach((movie) => println(movie)) //> Lady in the Water
//| Snakes on a Plane
//| You, Me and Dupree
ratings.keys.foreach(println) //> Lady in the Water
//| Snakes on a Plane
//| You, Me and Dupree
ratings.values.foreach((rating) => println(rating))
//> 3.0
//| 4.0
//| 3.5(6)获取所有key或value的集合
* 使用keySet keys keysIterator方法获取所有key
* 使用values valuesIterator
(7)反转键值
使用for/yield,可能会丢失数据
val reverseMap = for ((k,v) <- map) yield (v, k)(8)测试键值存在性
val states = Map(
"AK" -> "Alaska",
"IL" -> "Illinois",
"KY" -> "Kentucky") //> states : scala.collection.immutable.Map[String,String] = Map(AK -> Alaska,
//| IL -> Illinois, KY -> Kentucky)
if (states.contains("FOO")) println("Found foo") else println("No foo")
//> No foo
states.valuesIterator.exists(_.contains("ucky"))
//> res0: Boolean = true
states.valuesIterator.exists(_.contains("yucky"))
//> res1: Boolean = false(9)过滤键值
var x = collection.mutable.Map(1 -> "a", 2 -> "b", 3 -> "c")
//> x : scala.collection.mutable.Map[Int,String] = Map(2 -> b, 1 -> a, 3 -> c)
x.retain((k, v) => k > 1) //> res0: scala.collection.mutable.Map[Int,String] = Map(2 -> b, 3 -> c)
x.transform((k, v) => v.toUpperCase) //> res1: scala.collection.mutable.Map[Int,String] = Map(2 -> B, 3 -> C)
val y = x.filterKeys(_ > 2) //> y : scala.collection.Map[Int,String] = Map(3 -> C)
var m = Map(1 -> "a", 2 -> "b", 3 -> "c") //> m : scala.collection.immutable.Map[Int,String] = Map(1 -> a, 2 -> b, 3 -> c
//| )
m.filter((t) => t._1 > 1) //> res2: scala.collection.immutable.Map[Int,String] = Map(2 -> b, 3 -> c)
m.take(2) //> res3: scala.collection.immutable.Map[Int,String] = Map(1 -> a, 2 -> b)(10)排序
//默认存储无序的无法排序
val grades = Map("Kim" -> 90,
"Al" -> 85,
"Melissa" -> 95,
"Emily" -> 91,
"Hannah" -> 92) //> grades : scala.collection.immutable.Map[String,Int] = Map(Hannah -> 92, Mel
//| issa -> 95, Kim -> 90, Emily -> 91, Al -> 85)
import scala.collection.immutable.ListMap
ListMap(grades.toSeq.sortBy(_._1): _*) //> res0: scala.collection.immutable.ListMap[String,Int] = Map(Al -> 85, Emily -
//| > 91, Hannah -> 92, Kim -> 90, Melissa -> 95)
ListMap(grades.toSeq.sortWith(_._1 < _._1): _*)
//> res1: scala.collection.immutable.ListMap[String,Int] = Map(Al -> 85, Emily -
//| > 91, Hannah -> 92, Kim -> 90, Melissa -> 95)
ListMap(grades.toSeq.sortWith(_._1 > _._1): _*)
//> res2: scala.collection.immutable.ListMap[String,Int] = Map(Melissa -> 95, Ki
//| m -> 90, Hannah -> 92, Emily -> 91, Al -> 85)
ListMap(grades.toSeq.sortBy(_._2): _*) //> res3: scala.collection.immutable.ListMap[String,Int] = Map(Al -> 85, Kim ->
//| 90, Emily -> 91, Hannah -> 92, Melissa -> 95)
ListMap(grades.toSeq.sortWith(_._2 < _._2): _*)
//> res4: scala.collection.immutable.ListMap[String,Int] = Map(Al -> 85, Kim ->
//| 90, Emily -> 91, Hannah -> 92, Melissa -> 95)
ListMap(grades.toSeq.sortWith(_._2 > _._2): _*)
//> res5: scala.collection.immutable.ListMap[String,Int] = Map(Melissa -> 95, Ha
//| nnah -> 92, Emily -> 91, Kim -> 90, Al -> 85)
//TODO 看书_*关于_*
ListMap构造函数需要传入一个可变参数的2元元组sortWith和sortBy返回一个序列,内容为2元元组- _*目的将元组拆分为2元元组的可变参数
(11)找到最大键或值
val grades = Map("Al" -> 80, "Kim" -> 95, "Teri" -> 85, "Julia" -> 90)
//> grades : scala.collection.immutable.Map[String,Int] = Map(Al -> 80, Kim -> 9
//| 5, Teri -> 85, Julia -> 90)
grades.keysIterator.max //> res0: String = Teri
grades.max //> res1: (String, Int) = (Teri,85)
grades.valuesIterator.max //> res2: Int = 95
grades.keysIterator.reduceLeft((x, y) => if (x.length > y.length) x else y)
//> res3: String = Julia4、集(Set)
(1)添加元素
可变集
- 使用
+=++=add
不可变
- 使用
+++
(2)删除元素
可变集
- 使用
-=--= - 使用
retainclearremove方法
不可变集
- 使用
--- - 使用
filtertake方法
(3)使用可排序集
使用SortedSet
val s = scala.collection.SortedSet("cherry", "kiwi", "apple") //> s : scala.collection.SortedSet[String] = TreeSet(apple, cherry, kiwi)
5、队列
略
6、栈
略
7、Range
略
九、文件
1、打开并读取文件
简要写法:适用于scala脚本,文件不会关闭,随jvm关闭而关闭
import scala.io.Source
val fileName = "d:/test.txt" //> fileName : String = d:/test.txt
val buffer = Source.fromFile(fileName) //> buffer : scala.io.BufferedSource = non-empty iterator
for(line<-buffer.getLines()){
println(line) //> Line1
//| Line2
}
buffer.mkString //> res0: String = ""
//getLine返回一个迭代器自动关闭资源
def using[A<:{def close():Unit}, B](resource: A)(f:A=>B):B = {
try{
f(resource)
} finally {
resource.close()
}
} //> using: [A <: AnyRef{def close(): Unit}, B](resource: A)(f: A => B)B
val fileName = "d:/test.txt" //> fileName : String = d:/test.txt
val buffer = Source.fromFile(fileName) //> buffer : scala.io.BufferedSource = non-empty iterator
using(buffer)(_.mkString); //> res0: String = "Line1
//| Line2
//| "处理异常(用到上面的using方法)
// 将上定义 def using[A<:{def close():Unit}, B](resource: A)(f:A=>B):B
def readTextFile(fileName:String):Option[List[String]] = {
try{
val lines = using(io.Source.fromFile(fileName))( source => {
(for(line <- source.getLines()) yield line).toList
})
Some(lines)
} catch {
case e: Exception => None
}
} //> readTextFile: (fileName: String)Option[List[String]]
val fileName = "d:/test.txt" //> fileName : String = d:/test.txt
readTextFile(fileName) //> res0: Option[List[String]] = Some(List(Line1, Line2))其他io.Source.fromFile方法
略
2、写入文本文件
使用java的PrintWriter或FileWriter
3、读写二进制文件
使用java的FileInputStream和FileOutputStream
4、将字符串封装成文本文件对象,便于测试
import scala.io.Source
val fileName = "d:/test.txt" //> fileName : String = d:/test.txt
val buffer = Source.fromString("""Line1
Line2
""") //> buffer : scala.io.Source = non-empty iterator
for (line <- buffer.getLines()) {
println(line) //> Line1
//| Line2
}5、序列化
import java.io._
// 创建一个类
@SerialVersionUID(123L)
class Stock(var symbol: String, var price: BigDecimal)
extends Serializable {
override def toString = f"$symbol%s is ${price.toDouble}%.2f"
}
// (1) 创建一个实例
val nflx = new Stock("NFLX", BigDecimal(85.00))
// (2) 创建文件流,将对象序列化后写入文件
val oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("/tmp/nflx"))
oos.writeObject(nflx)
oos.close
// (3) 从文件中读取对象并实例化
val ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("/tmp/nflx"))
val stock = ois.readObject.asInstanceOf[Stock]
ois.close
// (4) 测试对象
println(stock)5、列出文件中目录
使用java方法
十、进程
1、执行外部命令
导入scala.sys.process
- 使用!方法执行命令,并获取退出码
- 使用!!方法执行命名,并获取输出
- 使用lines方法在后台执行命令,并得到输出
使用!
scala> "pwd".!
/c/Users/xxxx
res0: Int = 0
scala> val code = "pwd".!
/c/Users/xxxx
code: Int = 0
scala> code
res2: Int = 0
scala> Process("pwd").!
/c/Users/xxxx
res3: Int = 0
scala> Seq("pwd").!
/c/Users/xxxx
res4: Int = 0使用lines
val p = Process("pwd").lines注意:只能执行外部命令,不能执行内建命令如cd for
2、执行外部命令并使用标准输出
scala> val result = "ipconfig".!!
result: String =
"
Windows IP 配置
无线局域网适配器 WLAN:
媒体状态 . . . . . . . . . . . . : 媒体已断开连接
连接特定的 DNS 后缀 . . . . . . . : workgroup
无线局域网适配器 本地连接* 2:
媒体状态 . . . . . . . . . . . . : 媒体已断开连接
连接特定的 DNS 后缀 . . . . . . . :
以太网适配器 以太网:
连接特定的 DNS 后缀 . . . . . . . :
本地链接 IPv6 地址. . . . . . . . : fe80::24c3:eb4a:ec45:2b2e%18
IPv4 地址 . . . . . . . . . . . . : 172.19.208.233
子网掩码 . . . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.240.0
默认网关. . . . . . . . . . . . . : 172.19.208.1
隧道适配器 本地连接* 11:
连接特定的 DNS 后缀 . . . . . . . :
IPv6 地址 . . . . . . . . . . . . : 2001:0:5ef5:79fd:3c7d:1a4d:53ec:2f16
本地链接 IPv6 地址. . . . . . . . : fe80::3c7d:1a4d:53ec:2f16%17
默认网关. . . . . . . . . . . . . : ::
隧道适配器 isatap.{F8C49FBC-3672-45C1-86F5-68A03FD0F370}:
...3、其他略
十一、Actor和并发
1、Actor入门
import akka.actor.Actor
import akka.actor.ActorSystem
import akka.actor.Props
class HelloActor extends Actor {
def receive = {
case "hello" => println("hello back at you")
case _ => println("huh?")
}
}
object Main extends App {
// 初始化一个actor系统,并命名
val system = ActorSystem("HelloSystem")
// 创建并开启一个actor,名字叫helloactor,是HelloActor的一个实例
val helloActor = system.actorOf(Props[HelloActor], name = "helloactor")
// 给actor发送两个消息
helloActor ! "hello"
helloActor ! "buenos dias"
// 关闭actor系统
system.shutdown
}
/*输出
hello back at you
huh?
*/2、Actor之间通讯
import akka.actor._
case object PingMessage //来自ping的消息
case object PongMessage //来自Pong的消息
case object StartMessage //开始启动的消息
case object StopMessage //停止的消息
class Ping(pong: ActorRef) extends Actor {
var count = 0 //计数器
def incrementAndPrint { count += 1; println("ping") }
def receive = { //回复消息
case StartMessage => //接收到开始消息
incrementAndPrint //计数器++,
pong ! PingMessage //给pong发送消息
case PongMessage =>
incrementAndPrint
if (count > 99) {
sender ! StopMessage
println("ping stopped")
context.stop(self)
} else {
sender ! PingMessage
}
case _ => println("Ping got something unexpected.")
}
}
class Pong extends Actor {
def receive = {
case PingMessage =>
println(" pong")
sender ! PongMessage
case StopMessage =>
println("pong stopped")
context.stop(self)
case _ => println("Pong got something unexpected.")
}
}
object Main extends App {
val system = ActorSystem("PingPongSystem")
val pong = system.actorOf(Props[Pong], name = "pong")
val ping = system.actorOf(Props(new Ping(pong)), name = "ping")
// start the action
ping ! StartMessage
// commented-out so you can see all the output
Thread.sleep(1000);
system.shutdown
}
/*输出
ping
pong
......
ping stopped
pong stopped
*/3、Actor生命周期
import akka.actor._
class Kenny extends Actor {
println("进入 Kenny 构造函数")
override def preStart { println("kenny: preStart方法执行") }
override def postStop { println("kenny: postStop方法执行") }
override def preRestart(reason: Throwable, message: Option[Any]) {
println("kenny: preRestart方法执行")
println(s" 消息内容: ${message.getOrElse("")}")
println(s" 原因: ${reason.getMessage}")
super.preRestart(reason, message)
}
override def postRestart(reason: Throwable) {
println("kenny: postRestart方法执行")
println(s" 原因: ${reason.getMessage}")
super.postRestart(reason)
}
def receive = {
case ForceRestart => throw new Exception("Boom!")
case _ => println("Kenny 收到一个消息")
}
}
case object ForceRestart
object Main extends App {
val system = ActorSystem("LifecycleDemo")
val kenny = system.actorOf(Props[Kenny], name = "Kenny")
println("发送 kenny 一个简单的字符串消息")
kenny ! "hello"
Thread.sleep(1000)
println("让 kenny 重启")
kenny ! ForceRestart
Thread.sleep(1000)
println("停止 kenny")
system.stop(kenny)
println("关闭系统")
system.shutdown
}
/*输出
发送 kenny 一个简单的字符串消息
进入 Kenny 构造函数
kenny: preStart方法执行
Kenny 收到一个消息
让 kenny 重启
kenny: preRestart方法执行
消息内容: ForceRestart
原因: Boom!
kenny: postStop方法执行
进入 Kenny 构造函数
kenny: postRestart方法执行
原因: Boom!
kenny: preStart方法执行
[ERROR] [12/05/2016 23:22:35.325] [LifecycleDemo-akka.actor.default-dispatcher-7] [akka://LifecycleDemo/user/Kenny] Boom!
java.lang.Exception: Boom!
at Kenny$$anonfun$receive$1.applyOrElse(Main.scala:18)
at akka.actor.Actor$class.aroundReceive(Actor.scala:484)
at Kenny.aroundReceive(Main.scala:2)
at akka.actor.ActorCell.receiveMessage(ActorCell.scala:526)
at akka.actor.ActorCell.invoke(ActorCell.scala:495)
at akka.dispatch.Mailbox.processMailbox(Mailbox.scala:257)
at akka.dispatch.Mailbox.run(Mailbox.scala:224)
at akka.dispatch.Mailbox.exec(Mailbox.scala:234)
at scala.concurrent.forkjoin.ForkJoinTask.doExec(ForkJoinTask.java:260)
at scala.concurrent.forkjoin.ForkJoinPool$WorkQueue.runTask(ForkJoinPool.java:1339)
at scala.concurrent.forkjoin.ForkJoinPool.runWorker(ForkJoinPool.java:1979)
at scala.concurrent.forkjoin.ForkJoinWorkerThread.run(ForkJoinWorkerThread.java:107)
停止 kenny
关闭系统
kenny: postStop方法执行
*/- 构造函数:在第一个消息到来时实例化对象时调用
- preStart:启动前调用,重启后方法postRestart调用
- postStop:actor停止后调用,重启前方法preStart调用
- preRestart:在发生异常后调用
- postRestart:重启后调用postStop后,调用
启动流程 > 构造函数 -> preStart -> … -> postStop
重启流程 > preRestart -> postStop -> postRestart -> preStart
4、Actor启动
(1)主线程启动Actor
val system = ActorSystem("HelloSystem")
// 系统创建
val helloActor = system.actorOf(Props[HelloActor], name = "helloactor"(2)从Actor启动Actor
class Parent extends Actor {
val child = context.actorOf(Props[Child], name = "Child")
// more code here ...
}5、Actor停止
(1)actorSystem.stop(actor)或context.stop(actor)方法,处理完消息队列的消息然后停止
import akka.actor._
class TestActor extends Actor {
def receive = {
case _ => println("收到一个消息")
}
}
object Main extends App {
val actorSystem = ActorSystem("SystemStopExample")
val actor = actorSystem.actorOf(Props[TestActor], name = "test")
actor ! "hello"
// 停止
actorSystem.stop(actor)
actor ! "hello"
actorSystem.shutdown
}
//有两种可能输出
/*
1、
收到一个消息
收到一个消息
2、
收到一个消息
[INFO] [12/06/2016 22:41:44.804] [SystemStopExample-akka.actor.default-dispatcher-7] [akka://SystemStopExample/user/test] Message [java.lang.String] from Actor[akka://SystemStopExample/deadLetters] to Actor[akka://SystemStopExample/user/test#500643557] was not delivered. [1] dead letters encountered. This logging can be turned off or adjusted with configuration settings 'akka.log-dead-letters' and 'akka.log-dead-letters-during-shutdown'.
*/(2)传递PoisonPill消息,
import akka.actor._
class TestActor extends Actor {
def receive = {
case s: String => println("收到的消息: " + s)
case _ => println("TestActor 收到一个位置消息")
}
override def postStop { println("TestActor::postStop 方法执行") }
}
object Main extends App {
val system = ActorSystem("PoisonPillTest")
val actor = system.actorOf(Props[TestActor], name = "test")
// a simple message
actor ! "在 PoisonPill消息之前"
// the PoisonPill
actor ! PoisonPill
// these messages will not be processed
actor ! "在 PoisonPill消息之前"
actor ! "hello?!"
system.shutdown
}
/*
收到的消息: 在 PoisonPill消息之前
TestActor::postStop 方法执行
[INFO] [12/06/2016 22:44:47.361] [PoisonPillTest-akka.actor.default-dispatcher-4] [akka://PoisonPillTest/user/test] Message [java.lang.String] from Actor[akka://PoisonPillTest/deadLetters] to Actor[akka://PoisonPillTest/user/test#-390700988] was not delivered. [1] dead letters encountered. This logging can be turned off or adjusted with configuration settings 'akka.log-dead-letters' and 'akka.log-dead-letters-during-shutdown'.
[INFO] [12/06/2016 22:44:47.361] [PoisonPillTest-akka.actor.default-dispatcher-4] [akka://PoisonPillTest/user/test] Message [java.lang.String] from Actor[akka://PoisonPillTest/deadLetters] to Actor[akka://PoisonPillTest/user/test#-390700988] was not delivered. [2] dead letters encountered. This logging can be turned off or adjusted with configuration settings 'akka.log-dead-letters' and 'akka.log-dead-letters-during-shutdown'.
*/(3)gracefulStop ??方法,设置延时关闭,如果在指定实现内未关闭将报异常
import akka.actor._
import akka.pattern.gracefulStop
import scala.concurrent.{ Await, ExecutionContext, Future }
import scala.concurrent.duration._
import scala.language.postfixOps
class TestActor extends Actor {
def receive = {
case _ => println("TestActor 收到消息")
}
override def postStop { println("TestActor: postStop方法执行") }
}
object Main extends App {
val system = ActorSystem("GracefulStopTest")
val testActor = system.actorOf(Props[TestActor], name = "TestActor")
// try to stop the actor gracefully
try {
val stopped: Future[Boolean] = gracefulStop(testActor, 2 seconds, "stop")
//Await.result(stopped, 3 seconds)
for(i ← 1 to 10) testActor ! "xx"
println("testActor 被停止")
} catch {
case e: Exception => e.printStackTrace
} finally {
system.shutdown
}
}
/*
//Await.result(stopped, 3 seconds)
for(i <- 1 to 10) testActor ! "xx"
这样不会报异常
打开注释将会报异常
*/6、Actor系统关闭
//system.shutdown ,已废弃
system.terminate //关闭7、Actor监控子Actor死亡
(1)做法
context.watch(子Actor引用) //开启监控
case Terminated(kenny) //匹配消息
class Kenny extends Actor {
def receive = {
case _ => println("Kenny 收到一个消息")
}
}
class Parent extends Actor {
// start Kenny as a child, then keep an eye on it
val kenny = context.actorOf(Props[Kenny], name = "Kenny")
context.watch(kenny)
def receive = {
case Terminated(kenny) => println("OMG, Kenny被killed")
case _ => println("Parent 收到一个消息")
}
}
object Main extends App {
val system = ActorSystem("DeathWatchTest")
val parent = system.actorOf(Props[Parent], name = "Parent")
// 获取kenny的引用
val kenny = system.actorSelection("/user/Parent/Kenny")
kenny ! PoisonPill
Thread.sleep(5000)
println("calling system.shutdown")
system.terminate
}(2)获取子Actor
val kenny = system.actorSelection("/user/Parent/Kenny")
val kenny = context.actorSelection("../Kenny")
val kenny = system.actorFor("akka://DeathWatchTest/user/Parent/Kenny")
val kenny = system.actorFor(Seq("user", "Parent", "Kenny"))
val kenny = system.actorFor(Seq("..", "Kenny"))8、Futures实现并行计算任务
(1)简单实例会阻塞
import scala.concurrent.{ Await, Future }
import scala.concurrent.duration._
import scala.concurrent.ExecutionContext.Implicits.global
object Main extends App {
def sleep(time: Long) { Thread.sleep(time) }
// 使用 'time' 方法
implicit val baseTime = System.currentTimeMillis
// 2 - 创建一个 Future,相当于创建了一个新线程,主线程不会阻塞,且是call-by-name
val f = Future {
sleep(500)
1 + 1
}
// 3 - 这会阻塞,获得结果
val result = Await.result(f, 1 second)
println(result)
sleep(1000)
}(2)使用回调不阻塞
import scala.concurrent.{ Future }
import scala.concurrent.ExecutionContext.Implicits.global
import scala.util.{ Failure, Success }
import scala.util.Random
object Main extends App {
def sleep(time: Long) { Thread.sleep(time) }
println("开启一个计算")
val f = Future {
sleep(Random.nextInt(500))
42
}
println("onComplete方法前")
f.onComplete {
case Success(value) => println(s"转到了回调,参数为 = $value")
case Failure(e) => e.printStackTrace
}
// 做你剩下的工作
println("A ..."); sleep(100)
println("B ..."); sleep(100)
println("C ..."); sleep(100)
println("D ..."); sleep(100)
println("E ..."); sleep(100)
println("F ..."); sleep(100)
sleep(2000)
}
/*输出为:
开启一个计算
onComplete方法前
A ...
B ...
C ...
D ...
转到了回调,参数为 = 42
E ...
F ...
*/(3)回调方法
//同上......
f.onComplete {
case Success(value) => println(s"转到了回调,参数为 = $value")
case Failure(e) => e.printStackTrace
}
f onSuccess {
case result => println(s"成功的回调: $result")
}
f onFailure {
case t => println(s"失败回调: ${t.getMessage}")
}
//同上......
/*输出
开启一个计算
onComplete方法前
A ...
B ...
成功的回调: 42
转到了回调,参数为 = 42
C ...
D ...
E ...
F ...
*/(4)创建返回Future[T]实例的方法
import scala.concurrent.{ Await, Future, future }
import scala.concurrent.ExecutionContext.Implicits.global
import scala.util.{ Failure, Success }
object Main extends App {
def sleep(time: Long) { Thread.sleep(time) }
implicit val baseTime = System.currentTimeMillis
def longRunningComputation(i: Int): Future[Int] = future {
sleep(100)
i + 1
}
// 不阻塞
longRunningComputation(11).onComplete {
case Success(result) => println(s"result = $result")
case Failure(e) => e.printStackTrace
}
// keep the jvm from shutting down
sleep(1000)
}
/*输出:
result = 12
*/(5)运行多个任务,且有其他任务依赖他们,将所有任务连接一起
import scala.concurrent.{ Future, future }
import scala.concurrent.ExecutionContext.Implicits.global
import scala.util.{ Failure, Success }
import scala.util.Random
object Cloud {
def sleep(time: Long) { Thread.sleep(time) }
def runAlgorithm(i: Int): Future[Int] = future {
sleep(Random.nextInt(500))
val result = i + 10
println(s"从“云中”返回结果: $result")
result
}
}
object Main extends App {
def sleep(time: Long) { Thread.sleep(time) }
println("开始一组future")
val result1 = Cloud.runAlgorithm(10)
val result2 = Cloud.runAlgorithm(20)
val result3 = Cloud.runAlgorithm(30)
println("在 for-comprehension之前")
val result = for {
r1 <- result1
r2 <- result2
r3 <- result3
} yield (r1 + r2 + r3) //将三个任务完成后的结果的操作
println("在 onSuccess回调函数之前")
result onSuccess {
case result => println(s"total = $result")
}
println("在最后睡眠之前")
sleep(2000) // keep the jvm alive
}
/*输出:
开始一组future
在 for-comprehension之前
在 onSuccess回调函数之前
在最后睡眠之前
从“云中”返回结果: 20
从“云中”返回结果: 30
从“云中”返回结果: 40
total = 90
*/(6)连接器,将几个Future并行运算,并将结果连接起来
formapflatMapfilter等recoverrecoverWithfallbackTo提供错误处理机制
(7)给Actor发消息并等待消息回复
import akka.actor._
import akka.pattern.ask
import akka.util.Timeout
import scala.concurrent.{ Await, ExecutionContext, Future }
import scala.concurrent.duration._
import scala.language.postfixOps
case object AskNameMessage
class TestActor extends Actor {
def receive = {
case AskNameMessage => // respond to the 'ask' request
sender ! "Fred"
case _ => println("that was unexpected")
}
}
object Main extends App {
// 创建系统
val system = ActorSystem("AskTestSystem")
val myActor = system.actorOf(Props[TestActor], name = "myActor")
// (1) 询问actor方式1
implicit val timeout = Timeout(5 seconds)
val future = myActor ? AskNameMessage
val result = Await.result(future, timeout.duration).asInstanceOf[String]
println(result)
// (2) 另一种方法
val future2: Future[String] = ask(myActor, AskNameMessage).mapTo[String]
val result2 = Await.result(future2, 1 second)
println(result2)
system.shutdown
}
/*输出:
Fred
Fred
*/(8)使用become切换匹配函数
import akka.actor._
case object ActNormalMessage
case object TryToFindSolution
case object BadGuysMakeMeAngry
class DavidBanner extends Actor {
import context._
def angryState: Receive = {
case ActNormalMessage =>
println("Phew, I'm back to being David.")
become(normalState)
}
def normalState: Receive = {
case TryToFindSolution =>
println("Looking for solution to my problem ...")
case BadGuysMakeMeAngry =>
println("I'm getting angry...")
become(angryState)
}
def receive = {
case BadGuysMakeMeAngry => become(angryState)
case ActNormalMessage => become(normalState)
}
}
object Main extends App {
val system = ActorSystem("BecomeHulkExample")
val davidBanner = system.actorOf(Props[DavidBanner], name = "DavidBanner")
davidBanner ! ActNormalMessage // init to normalState
davidBanner ! TryToFindSolution
davidBanner ! BadGuysMakeMeAngry
Thread.sleep(1000)
davidBanner ! ActNormalMessage
system.shutdown
}
/*输出:
Looking for solution to my problem ...
I'm getting angry...
Phew, I'm back to being David.
*/(9)并发集合
scala> val v = Vector.range(0, 10)
v: scala.collection.immutable.Vector[Int] = Vector(0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9)
scala> v.foreach(print)
0123456789
scala> v.par.foreach(print)
5678901234
scala> v.par.foreach(print)
0123456789
scala> v.par.foreach{ e => print(e); Thread.sleep(50) }
0516273894